Revolutionary ‘green’ types of bricks and construction materials could be made from recycled PVC, waste plant fibres or sand with the help of a remarkable new kind of rubber polymer discovered by Australian scientists.
The rubber polymer, itself made from sulphur and canola oil, can be compressed and heated with fillers to create construction materials of the future, says organic chemistry researcher Flinders University Associate Professor Justin Chalker.
“This method could produce materials that may one day replace non-recyclable construction materials, bricks and even concrete replacement,” he says, unveiling the promising new technique in a journal paper just published in Chemistry – A European Journal.
The powdered rubber can potentially be used as tubing, rubber coatings or bumpers, or compressed, heated then mixed with other fillers to form entirely new composites, including more sustainable building blocks, concrete replacement or insulation.
Cement is a finite resource and heavily polluting in its production, with concrete production estimated to contribute more than 8 per cent of global greenhouse gases emissions, and the construction industry worldwide accounting for about 18 per cent.
“This is also important because there are currently few methods to recycle PVC or carbon fibre,” he says, with collaborators from Flinders, Deakin University and University of WA.
“This new recycling method and new composites are an important step forward in making sustainable construction materials, and the rubber material can be repeatedly ground up and recycled,” says lead author Flinders PhD Nic Lundquist. “The rubber particles also can be first used to purify water and then repurposed into a rubber mat or tubing.”
Co-author and research collaborator Dr Louisa Esdaile says the important research looks at ways to repurpose and recycle materials, so that these materials are multi-use by design.
“Such technology is important in a circular economy,” says Dr Esdaile, a special contributor to this month’s Young Chemist issue of Chemistry – A European Journal (ChemEurJ).
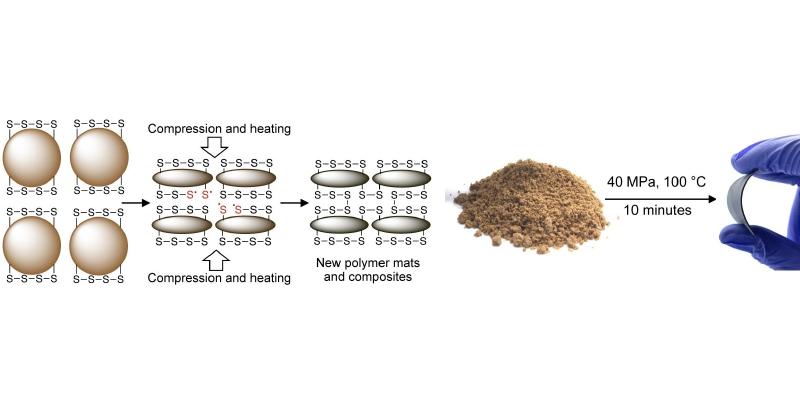
The new manufacturing and recycling technique, labelled ‘reactive compression molding,’ applies to rubber material that can be compressed and stretched, but one that doesn't melt. The unique chemical structure of the sulphur backbone in the novel rubber allows for multiple pieces of the rubber to bond together.
The project started two years ago in the Chalker Laboratory as a third-year project by Ryan Shapter, with Flinders University PhD candidates Nicholas Lundquist and Alfrets Tikoalu and others contributing to the paper in this month’s special Young Chemist issue of ChemEurJ.
The Chalker Lab at Flinders University has previously developed sulphur polymers for a number of applications in mopping up environmental pollutants – from oil spills in water and mercury and heavy metals in soil.